The Central lowland belt (Central Belt) is the densely populated and heavily industrialized population center and economic heart Scotland. Between the cities Glasgow, the Scottish capital Edinburgh and Dundee About three quarters of all Scots live. The central lowland belt borders the to the south Southern Uplands and in the north to the Highlands and North East Scotland. In the west and east it meets the sea, but more in the form of sea bays that cut deep into the land (Firth of Clyde in the west, Firth of Forth in the east) than the open sea.
&groups=Maske,Track,Aktivitaet,Anderes,Anreise,Ausgehen,Aussicht,Besiedelt,Fehler,Gebiet,Kaufen,Kueche,Sehenswert,Unterkunft,aquamarinblau,cosmos,gold,hellgruen,orange,pflaumenblau,rot,silber,violett)
Regions
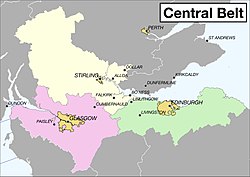
- Clydeside - Greater Glasgow is the industrial heart and population center of Scotland. Here you can see industrial history, concrete excesses of the 1960s and a varied coastal landscape in the transition to the highlands.
- Lothian - The counterpart on the east coast is the greater Edinburgh area with evidence of power, as befits the capital, between the Firth of Forth and the hills of the Borders.
- Stirlingshire and Clackmannanshire - The isthmus between the west and east coasts is the historic heart of Scotland, anyone who moved between the regions had to pass through here and so many of the battles for Scottish independence were fought here
places
The two largest cities in the country Edinburgh, political center and Glasgow, industrial center (in English: "Edinburgh is the capital, Glasgow has the capital") dominate the region as a focus for residents and a magnet for visitors.
1 Edinburgh (480,000 inhabitants / metropolitan area 750,000 inhabitants), located in the east on the Firth of Forth, has been the capital of Scotland since the late Middle Ages and is now home to the Scottish regional parliament. In addition, Edinburgh is now a financial center with the headquarters of several banks and insurance companies, the growth of which has left a noticeable dent since 2008 with the financial crisis. With the castle, the old town, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, as well as the (at 250 years old, not quite young) new town, numerous museums, the former royal yacht Britannia in the port of Leith and the world-famous festival, Edinburgh is a top visitor magnet.
2 Glasgow (600,000 inhabitants / metropolitan area 2.8 million, that's every second Scotsman), located in the west on the Firth of Clyde, is an important industrial and port city that has long been dominated by shipbuilding. The self-confident metropolis, which for a long time competed with Liverpool for second place in the Empire (or, like the Glaswegian says: "Second city in the Empire, I think its London ...". Glasgow was European Capital of Culture in 1990 and not only has a lively music scene, from which bands like the "Simple Minds" emerged, but also numerous museums and magnificent architecture from the 19th century, Art Nouveau (namely by the Glasgow architect Charles Mackintosh and remarkable revitalization of the port area in the last few decades.
3 Falkirk (36,000 inhabitants) - busy industrial city
4 Paisley (80,000 inhabitants) Bishopric and city of the textile industry in the vicinity of Glasgow
5 Cumbernauld (50,000 inhabitants) - a dormitory city for Glasgow that was built on the drawing board in the 1960s with a huge shopping mall and the most hideous architecture in the country
6 Stirling![]() (50,000 inhabitants) with its castle is a historic center and another former capital of Scotland and a self-proclaimed gateway to the Highlands.
(50,000 inhabitants) with its castle is a historic center and another former capital of Scotland and a self-proclaimed gateway to the Highlands.
7 East Kilbride - (75,000 inhabitants), dormitory town in the Glasgow suburb with by far the largest mall far and wide
Other goals
- 8 Balloch (6,000 inhabitants), popular excursion destination for the Glaswegians on the southern foothills of the Loch Lomond
- 9 Linlithgow (13,000 inhabitants) with the ruins of Maria Stuart's palace
- 10 Roslin (1,500 inhabitants), village south of Edinburgh and birthplace of the clone sheep Dolly
- 11 Wemyss Bay (1,000 inhabitants), Fin de Siecle place of residence and ferry port doon de watter with the most beautiful train station in Scotland
background
The Central Belt describes the part of Scotland between the Firth of Clyde in the west and the Firth of Forth in the east of the country. Even if it is geographically and historically not the "central" part of Scotland (which would be a little further north around Perth), the most important centers of the country are here with the capital Edinburgh in the east and the industrial center Glasgow in the west with its enormous cultural wealth.
Rich coal deposits were the basis for intensive industrialization since the end of the 18th century, which, coupled with the Scottish ingenuity (including the steam engine), had a lasting impact on the region. Seven of the ten largest cities in Scotland are in this belt. It is by far the most densely populated part of the country and has a dense infrastructure, including the two important airports in the country.
For visitors, the region offers a wide range of historical sites, cultural treasures in the museums and castles, impressive sacred buildings as well as evidence of industry and engineering. In terms of landscape, the region, which is also known as the "Lowlands", is not very spectacular, but it is particularly lovely on the coasts and in the transition area to the hills of the Southern Uplands. However, the northern part of Stirlingshire already extends into the Highlands into it.
language
getting there
The two largest cities in Scotland - Edinburgh and Glasgow - are located in the Central Belt and, with their airports and train stations, offer transport connections from all over the United Kingdom as well as from the European continent. Detailed travel information can be found in the relevant local articles.
The one about 170 km south of Edinburgh Newcastle upon Tyne is the closest ferry port to any Central Belt destination.
The Central Belt can be reached by road from the south either on the ![]() from Carlisle in 155 km to Glasgow or from Newcastle on the
from Carlisle in 155 km to Glasgow or from Newcastle on the ![]() through the country or
through the country or ![]() along the coast in about 170 km.
along the coast in about 170 km.
The railway lines also run along the coast (East Coast Main Line from Newcastle to Edinburgh or West Coast Main Line from Carlisle to Glasgow with a branch to Edinburgh).
mobility
Scot Rail offers a dense regional network within the region as well as to the rest of the Scottish country.
Tourist Attractions
.jpg/250px-FalkirkWheelSide_2004_SeanMcClean_(jha).jpg)

- Falkirk Wheel. Ship lift in the design of a ferris wheel. Connects at Falkirk the Union Canal and the Forth and Clyde Canal.
- 1 Firth of Forth Rail Bridge (Forth Bridge). In 1890 the railway bridge over the Firth of Forth was completed. It has a span of 2.5 km and consists of 54,000 tons of steel. The bridge has been part of the UNESCO world cultural heritage.

- Antonine Wall. Similar to the Hadrian's Wall a fortification from Roman times against invaders from the north, which leads on the shortest connection from the Firth of Forth to the Firth of Clyde (e). Unesco world heritage site
- Pineapple House at Dunmore, Summer home of the Earls of Dunmore with a pineapple domed roof, one of the most bizarre houses in Scotland
- Crichton Castle, Midlothian.

Dec2005.jpg/350px-Stirling(DonaldMacDonald)Dec2005.jpg)
