| Location | |
 | |
| Ensign | |
 | |
| Basic information | |
| Capital | Santo Domingo |
| Goverment | Representative democracy |
| Currency | Dominican peso (DOP) |
| Area | total: 48,730 km2 soil: 48,380 km2 country: 350 km2 |
| Population | 9.904.000 (2008) |
| Language | Spain |
| Religion | Roman Catholic 95% |
| Power system | 110/60Hz (American model) |
| Phone number | 1-809 1-829 1-849 |
| Internet TLD | .do |
| time zone | UTC/GMT -4 hours |
Dominican Republic is a country belonging to Americas.Dominican Republic ( .) Spain: República Dominicana, English: Dominican Republic) is a country in the Caribbean. The western third of the island of Hispaniola belongs to Haiti, making Hispaniola one of only two Caribbean islands belonging to two countries. Both in area and population, the Dominican Republic is the second largest Caribbean country (after Cuba), with 48,442 km and an estimated population of 10 million.
overview
Home to the Taínos since the 7th century, the territory of the Dominican Republic was established by Christopher Columbus in 1492 and became home to the first permanent European settlement in the Americas, named Santo Domingo , the capital of the country and the first capital of Spain in the New World. In Santo Domingo, among other firsts in the Americas, first university, first church, and first castle, there was also the first UNESCO World Heritage site. After three centuries of Spanish rule, alternating between Haitian and French periods, the country became independent in 1821 but was quickly invaded by Haiti. It regained its independence in 1844, but experienced mainly political turmoil and autocracy, and also briefly returned to Spanish rule, for the next 72 years. The US occupation period 1916-1924 and followed by the military dictatorship of Rafael Leonidas Trujillo Molina until 1961. The last civil war in 1965, which ended with the intervention of the United States, and followed by the dictatorial rule of Joaquín Balaguer until 1978. Since 1978, the Dominican Republic has transitioned to a representative democracy.
The Dominican Republic has also adopted a liberal economic model, which has made it the largest economy in the region. Although long known for its sugar production, its economy Today it is mainly the service sector, with a modern telecommunications system. However, unemployment, corrupt authorities, unfair income distribution, and inadequate electricity supply remain major problems in Dominicana.
International migration brings a lot of influence to these countries, as the country is the source and destination of both major migration flows. Haitian immigration and the integration of Haitian Dominicans are big issues; The total population of Haitian ancestry is estimated at 800,000. There is a large diaspora, mainly in the United States, where it is about 1.2 million.[8] They help develop the nation by sending billions of dollars to their families, one tenth of Dominica's GDP.[6][9] The Dominican Republic has become the Caribbean's largest tourist destination; Year-round golf courses are among the top attractions. The country has the highest mountain in the Caribbean, Pico Duarte, as well as Lake Enriquillo, the Caribbean's largest lake. Quisqueya, as the Dominicans often call their country, has a mild average temperature (26 °C) and is well-suited to biodiversity.[10] Music and sport are of the highest importance. in Dominican culture, with the merengue being the national anthem and dance and also baseball being the preferred sport.
History
In 1492, Cristoforo Colombo discovered this island and named it La Espanola (Hispaniola); Colombo's son, Diego became the first Viceroy of the island. The capital Santo Domingo, founded in 1496, is the oldest European settlement in the Western Hemisphere. The island was a Spanish colony until 1697. The Treaty of Ryswick divided the island into two parts: the eastern Spanish territory (Santo Domingo) and the western French territory (Haiti).
In 1795, Spain was forced to hand over the eastern territories to France.
In 1801, Toussaint Louverture and the island's slaves revolted and took control of the island. In 1809, the Dominicans defeated the French and established the first republic. In 1814, Spain recaptured the eastern part. In 1821, the immigrants declared independence for the 'Dominican Republic. In 1822, the Haitians invaded Santo Domingo and annexed the territory to Haiti.
The independent republic, proclaimed in 1844, experienced a tumultuous historical period: Spain returned to conquest (1861-1865); economic and political difficulties facilitated the US military intervention and occupation (1916-1924). General Rafael Trufillo, with the backing of the United States, established a totalitarian dictatorship. In 1961, Trufillo was assassinated. In 1963, the military overthrew President Juan Bosch. The period of political instability resumed and the United States again intervened militarily (1965) to end the civil war. Armed conflicts ended after the defeat of the guerrillas in 1973. Joaquin Balaguer has served as President since 1966 and has maintained power based on the military. In 1978, J. Balaguer ceded the presidency to Guzmán Fernández. In 1982, Jorge Blance succeeded G. Fernández. In 1986, J. Balaguer was re-elected President. In 1996, the presidency belonged to Leonel Fernández. In 2000, Hipólito became the new leader of the Dominican Republic.
Geography[edit]The Dominican Republic is an island nation in the Caribbean Sea, located to the east and occupying two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola. The western third of Hispaniola is the country of Haiti. The topography of this island nation consists of a coastal plain, four nearly parallel mountain ranges stretching west-east, the fertile black soil valley of Cibao spreading to the north of the Cordillera Central range.
Politic
Economy
As a slow-growing economy, dependent on the US.
Although sugar production is a traditional economic sector, now nickel and iron have become the main exports. Dominica is the leading country in Latin America and 5th in the world in terms of gold mining; production power reached 6.7 billion kWh, consumed 6.7 billion kWh. Tourism is the industry that earns the most foreign currency; exports reached 1 billion USD, imports 3.6 billion USD, foreign debt: 3.6 billion USD.
Products from industrial crops (sugar cane, coffee, cocoa, tobacco) and nickel are the main export sources of the island. The establishment of about 40 industrial export processing zones and the development of tourism create an undeniably dynamic economy. However, living standards are still low, inflation is high, and the economy is heavily dependent on the United States.
Region
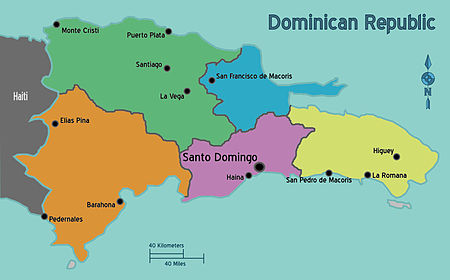
| Urban area Urban area and surrounded by beaches. |
| East Plains and East Coast |
| East Cibao and the Gulf of Samaná The beautiful bay is often likened to "Heaven on Earth" |
| West Cibao and the North Coast The second largest city, the highest mountain in the Caribbean. |
| Enriquillo Valley and the South |
City
- Santo Domingo - capital
- Higüey
- Juan Dolio
- Puerto Plata
- Punta Cana
- San Pedro de Macoris
- Santa Barbara De Samana
- Santiago de los Caballeros
- Sosua
- Rio San Juan
- La Romana - 3rd largest city
- Hi Adrianna Island
Other destinations
- Bayahibe
- Bonao
- Cabarete
- Constanza
- Dominicus
- Jarabacoa
- Las Terrenas
- Las Galeras
- Michael
- Bahia de las Aguilas
- Playa Bonita
Arrive
Citizens of most countries can purchase a tourist card upon arrival. See entry requirements [1]
By air
The main airports (in alphabetical order) are:
- (AZS) Samana, also known as "El Catey", is located between the towns of Nagua and Samana on the north coast.
- (EPS) Samana, also known as "Aeropuerto Internacional Arroyo Barril" between Sanchez and Samaná
- (JBQ) "La Isabela" airport in Santo Domingo, mainly for domestic flights but also receive some flights from other Caribbean islands
- (LRM) La Romana on the southeast coast
- (POP) Puerto Plata, also known as "Gregorio Luperon" on the north coast
- (PUJ) Punta Cana . International Airport in the east, the busiest in the country
- (SDQ) Santo Domingo, also known as "Las Americas" on the south coast near the capital city Santo Domingo
- (STI) Santiago is also known as "International Cibao" in Santiago de los Caballeros (the country's 2nd largest city).
- (Because of) Constanza, a domestic airport for all Dominica locations.
- (BRX) Barahona, also known as "Aeropuerto Internacional María Montez" This airpot was reopened during the Haiti earthquake, to bring initial support to the Haitian people.
- (CBJ) Cabo Rojo, Pedernales, for domestic use only, located near the harbor of Cabo Rojo.
You can get flights from Europe via Madrid (MAD) or Paris (CDG). From the US you can fly from New York, Ft. Lauderdale, Miami, Philadelphia, San Juan, Atlanta nice Charlotte. Cities most of Europe and Canada have charter flights, operating seasonally.
You will have to pay 10 USD for a tourist card on arrival. This card must be paid in US dollars or euros. Local currency, sterling, or other currencies will not be accepted. US$20 exit tax. Cash flow is paid on most scheduled and chartered flights. If you're flying on a US airline, departure tax is always included in the taxes when you buy your ticket, so you won't have to pay anything when you leave.
Taxi fares to nearby hotels are posted just outside the airport.
Taxi from the airport to Santo Domingo (Ciudad Colonial): the price is about 40 USD. There are no hotel buses for airport transfers in the Dominican Republic.
At the airport you can exchange your US dollars and euros in Dominican Pesos. Note that you may not be able to exchange back local currency to US dollars and euros, so do so before leaving.
