 | |
| Location | |
_(-mini_map_-rivers).svg/250px-India_in_Asia_(de-facto)_(-mini_map_-rivers).svg.png) | |
| Ensign | |
 | |
| Basic information | |
| Capital | New Delhi |
| Goverment | Federal Parliamentary Republic |
| Currency | Indian Rupee (र) |
| Area | total: 3,287,590 km2 soil: 2,973,190 km2 country: 314,400 km2 |
| Population | 1,205,073,612 (as of July 1, 2012) |
| Language | Hindi, English and 21 other languages |
| Religion | Hindu 80.5%, Muslim 13.4%, Christian 2.3%, Sikh 1.9%, other groups including Buddhist, Jain, Parsi 1.9% (2012) |
| Power system | 230V/50Hz, Indian (Old British)/European plugs |
| Phone number | 91 |
| Internet TLD | |
| time zone | UTC 5.5 |
India (Hindi: गणराज्य Bharat; Chinese called: Tianzhu (天竺), Juan Du (身毒)) is a country South Asia, occupies most of the Indian peninsula. India has a boundary with Pakistan, China, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan and Afghanistan. India is the second most populous country in the world, with a population of over one billion, and at the same time the seventh largest by area.
overview
The Republic of India appeared on the world map on August 15, 1947. The establishment of the state of India was the culmination of the struggle of the people in India. South Asia to escape the yoke of the British Empire. India has a civilization of the Indus River (Indus) that flourished 5 thousand years ago. India is the birthplace of four important world religions: Hinduism (Hindu), Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism. Before independence, India was part of the British Indian subcontinent. The founding of this nation was greatly attributed to Mohandas Gandhi, who was hailed as the "father of India". He persuaded the British government to grant India independence by peaceful and acceptable way. But Britain decided to split India into two countries: one with a majority Hindu population, India; One with a Muslim majority was Pakistan, which in turn consisted of two parts: the eastern part of India called East Pakistan (later known as East Pakistan). Bangladesh), the western part called West Pakistan (present-day Islamic Republic of Pakistan). These two territories are separated by more than 2000 km across the Indian territory.
History
Stone Age settlements with paintings at Bhimbetka, Madhya Pradesh are the earliest known traces of human life in present-day India. The earliest known permanent settlements appeared 9,000 years ago, and gradually evolved into the Indus Valley Civilization, which began around 3300 BC and culminated between 2500 BC and 1500 BC. The cities of this culture have urban and scientifically advanced features such as high-level civil drainage systems. It was followed by the Vedic Civilization, created by the Indo-Aryan tribes who founded the ancient foundations of Hinduism and other cultural aspects. In ancient Vedic texts and Indian mythology, the land is considered Bharatavarsha. From around 550 BC, many independent kingdoms such as the Mahajanapadas were established throughout the country. The country has a very complex religious culture, the birthplace of Jainism and Buddhism. Ancient schools appeared in Taxila, Nalanda, Pataliputra and Ujjain.
At the end of the 3rd century BC, the Mauryan dynasty of Chandragupta Maurya and Ashoka the Great unified most of present-day South Asia. From 180 BC, a series of attacks from Central Asia by the Indo-Greeks, Indo-Scythians, Indo-Parthians and Kushans occurred in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent. From the 3rd century BC, the Gupta dynasty ruled during what is considered the "Golden Age" in ancient Indian history. In the south, the Chalukya, Rashtrakuta, Chera, Chola, Pallava and Pandya dynasties emerged at different stages. Science, mechanics, art, literature, mathematics, astronomy, religion, and philosophy flourished under the rule of this dynasty.
The Sanchi Tower at Sanchi, Madhya Pradesh was built by the emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC. After the invasions from Central Asia, between the 10th and 12th centuries, much of northern India came under the rule of the Sultanate of India. Delhi and the Mughal Empire. Under Akbar the Great, Indian economy and culture developed continuously along with the policy of religious harmony. The Mughal emperors also gradually extended their control over the entire Indian subcontinent. However, many native kingdoms also thrived, especially in the south, such as the Vijayanagara Empire or the Maratha Empire. During the 18th and 19th centuries, many countries Europe, consisting of Portugal, the Netherlands, France and Great Britain, first came to India as merchants, then took advantage of the discord in relations between the kingdoms to establish colonies. location in India. By 1856, most of India was under the control of the British East India Company, with its capital at Calcutta. A year later, military uprisings took place everywhere, the Indians called it the First War of Independence (in English called Sepoy Mutiny), the uprising was unsuccessful because it seriously threatened. respect British rule. Thus India was directly administered by the British Empire.
In the early 20th century, a struggle for independence was waged by the National Congress of India, led by such Indians as Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Mahatma Gandhi, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel and Jawaharlal Nehru. Millions of dissidents engaged in civil disobedience campaigns under the oath of ahimsa - nonviolence - and they did just that. Gandhi would lead the Indian people on the Dandi Salt March (Dandi Salt March) to challenge the salt tax, and a 1942 nationwide uprising demanding that Britain "Leave India". India regained its independence on August 15, 1947 - 565 small states ruled by princes united with the British colonial provinces to form a single nation, but only after the provinces had A number of Muslims split, as a result of the separatist campaign led by the Muslim League, to form Pakistan. Since independence, India has repeatedly faced sectarian violence and rebellions in many parts of the country, but it has remained united and democratic. India had an unresolved border dispute with China, which escalated into a brief Sino-Indian War in 1962; and with Pakistan, leading to wars in 1947, 1965, 1971 and 1999 in Kargil. India is a founding member of the Non-Aligned Movement and the United Nations. In 1974, India conducted underground nuclear weapons tests, making it an unofficial member of the "nuclear club". They then conducted five more tests in 1998. The remarkable economic reforms that had taken place since 1991 made India one of the fastest growing economies in the world, increasing its position their position in the region and around the world.
Geography
The territory of India occupies a large part of the Indian subcontinent, lying on the Indian Plate, the northern part of the Indo-Australian Plate, south of South Asia. The northern and northeastern states of India are partly located in the Himalayas. The remainder in the north, central and eastern India consists of the fertile Indo-Gangetic plains. To the west, the southeastern border of Pakistan, is the Thar Desert. The southern part of Peninsular India consists of the entire Deccan Plateau, bordered by two coastal mountain ranges, the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats.
India is the source of many great rivers, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Yamuna, Godavari, Kaveri, Narmada and Krishna. India has three archipelagos – Lakshadweep off the southwest coast, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the southeast volcanic island range and the Sunderbans in the Ganges Delta in West Bengal.
Climate
India's climate varies from tropical in the south to temperate in the north, the high altitude northern regions often experience long periods of snowfall. The Indian climate is heavily influenced by the Himalayas and the Thar Desert. The Himalayas, along with the Hindu Kush Mountains in Pakistan, are a natural barrier that blocks cold winds from Central Asia. They make much of the Indian continent warmer than most other places of the same latitude. The Thar Desert causes the southwest monsoon to bring a lot of moisture into the Indian mainland causing rain from June to September.
The diverse climate is the reason why India is listed as the country with the highest biodiversity in the world, both in terms of species and number of individuals. The number of species of flora and fauna in the Indian subcontinent is second only in the world after the whole world Africa, and there are many species present only here. India is now home to more than 3000 Bengal tigers and 10,000 elephants Asia and about 8000 gaurs, the rarest animals in the world.
Politic
India is the largest federal democracy in the world, consisting of 28 states and 7 territories. The states have their own autonomy and legislative power, but national laws have more power than the laws of the states. India has three branches of government: Legislative, Executive and Judiciary at the state and national level. The President is the head of state, the protector of the constitution and the Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces. The President and Vice President are elected indirectly by an electoral college for five-year terms. The Indian Parliament is bicameral, with a popularly and directly elected lower house, known as the Lok Sabha (People's Parliament), elected for a term of five years, and the upper house, Rajya Sabha (Association). national council), elected alternately for six-year terms by a council of national legislative members.
The Prime Minister is the head of government and has the greatest executive power. The prime minister is elected by the legislators of the political party or parliamentary majority coalition, and serves a five-year term. The Constitution does not specify the title of Deputy Prime Minister, but this title still exists in practice. All Indian citizens over the age of 18 are eligible to vote. The Prime Minister leads the Council of Ministers. Any minister must be a member of the lower house or parliament. In the Indian parliamentary system, the executive is subordinate to the legislature.
Region
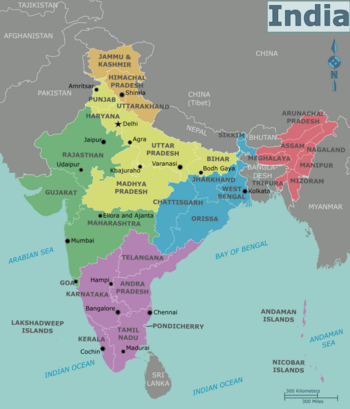
| North Himalayas (Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand) Mountainous and beautiful, a tourist destination for the adventurous and spiritual. This area has some of India's most visited hill stations and religious places. Covers the country sharp scenic spots. |
| The Plains (Bihar, Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh) The national capital Delhi is here. The Ganges and Yamuna rivers flow through this plain. Many of the historical figures shaped by India took place in this region. |
| West India (Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan) Miles of the Thar Desert. Home to colorful palaces, forts, Rajasthan, the country's largest and most vibrant city Mumbai (formerly known as Bombay), the enchanting rock-cut caves of Ajanta and Ellora, the wonderful primeval forests the beaches of Goa and Bollywood and last but not least, the excellent state of Gujarat the Asian lion house and a business center with the fastest - growing city of Ahmedabad and Surati. |
| South India (Andaman and Nicobar, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep, Pondicherry, Tamil Nadu) South India is famous for its famous and historic temples, rainforests, mountainous beaches, and vibrant cities. Bangalore, Chennai and Hyderabad. The island groups of Andaman & Nicobar (to the east) and Lakshadweep to the west are included in this area for convenience, but they are far from the mainland and have their own unique characteristics. |
| East India (Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Sikkim, West Bengal) Economically underdeveloped, but culturally rich and perhaps the most welcoming to outsiders. Kolkata (formerly known as Calcutta), once the capital of British India, and the temple cities of Puri, Bhubaneswar and Konark. The geography stretches from the mountains to the coast, leading to an interesting change in climate. It is also India's mineral stockpile, having the country's largest and richest mines. |
| Northeast India (Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura) Island and relatively pristine, tribal corner of the country, with greenery, beautiful landscapes, endemic plants and animals of Indo-Malay groups and famous for Tea garden. Consists of seven small states (by Indian standards, some of which are larger than Switzerland or Austria) popularly nicknamed the Seven Sisters |
City
- Delhi - the capital of India and the center of North India.
- Bangalore - the garden city, once a residential area for retirees, has now become a city of pubs, technology and companies.
- Chennai - the main port in South India, the cradle of Carnatic music and Bharatanatyam, with the famous Marina beach, the automotive capital of India and a rapidly emerging IT hub.
- Hyderabad - famous for pearl and diamond mall. Industrialization brought major Indian financial and manufacturing facilities to the city and quickly emerged as an IT hub.
- Jaipur - Pink City is a great exhibition of Hindu Rajput culture of medieval Northern India.
- Kochi - Queen of the Arabian Sea, historically a center of international trade, at the gateway to the sandy beach.
- Kolkata - the cultural capital of India, Kolkata is home to many colonial buildings. It's called Joy's City.
- Mumbai - the financial capital of India, the center of cinema "Bollywood".
- Varanasi - considered the holiest Hindu city, located on the banks of the Ganges River, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world.
- Agra, the city has three World Heritage Sites, especially the Taj Mahal
Other destinations
India has many outstanding landmarks and regions of outstanding beauty. Here is a list of the nine most notable:
- Bodh Gaya — (Bodhidharma) where Shakyamuni Buddha attained enlightenment.
- Ellora / Ajanta - Spectacular rock-cut monasteries and temples, holy places for Buddhism, Jainism and Hinduism.
- Goa - an East-West mix, beach and syncretic culture.
- Golden Temple - where Sikh saints are located Amritsar
- Hampi - amazing ruins of Vijayanagara empire
- Khajuraho - famous for its erotic sculptures
- Konark - Temple of the Sun, the only example of Kalingan Architecture, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Lake Palace - Lake Palace of the famous Octopussy, located in Udaipur
- *Meenakshi Amman Temple/Meenakshi Sundareswarar Temple - a spectacular Hindu temple in Madurai
- Taj Mahal - marble mausoleum not two in Agra. One of the Seven Wonders of the Modern World.
Arrive
Do you need a visa?
Tourist Visa on Arrival (TVOA)
Need a visa
|
Visa
Depending on the purpose of your visit, you may be able to obtain a tourist visa (six months), a business visa (6 months, one year or more, multiple entries) or a student visa (up to 5 years). A special 10-year visa ($150, business and tourist) is available only to US citizens. The India Visa is valid from the date it is issued, not the date of entry. For example, a 6-month visa issued on June 1 will expire on June 30, regardless of your date of entry. There is a minimum gap period of two months between consecutive tourist visas. A 6-month tourist visa can have a maximum stay of 90 days at a time, depending on nationality. Be sure to check the maximum time for one visit with your local embassy.
As of 1 January 2010, India has introduced a new TVOA scheme (visitor visa on arrival), which is available to citizens of Finland, Japan, New Zealand, Luxembourg, Singapore, Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Indonesia and the Philippines at airports in Chennai, Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata for a stay of up to 30 days. It may take some time (no assembly time, allow 1-6 hours) to process the application once you have arrived at the airport. The Tova Visa costs 60 USD, is valid for one time and is non-renewable. In addition, there is a minimum gap between the two months of expiration of a tourist visa and the subsequent issuance. Please contact your country's embassy/consulate for more information.
Many Indian embassies have visa processing outsourced in whole or in part to third party companies, to check before going to the embassy. For example, in the US, you must submit your visa application to Travisa, not the embassy. Applying for a visa through these agencies also attracts a visa application fee, which is detailed on most embassy websites and should be checked before submitting your documents. Also, many Indian embassies only offer visas to residents of that country: this means you'll get your visa before you leave home, instead of trying to get in a neighboring countries (although, as in August '09, non-residents can apply for a visa through the Bangkok embassy for an additional 400 THB "referral fee").
Visa rules and values will vary based on nationality. Check the website of the Indian Embassy, consulate or high commission in your country or contact your local office.
By air
From Vietnam, there is no direct flight to India, but often have to transit in Bangkok, Kuala Lumpur or Singapore.
The main air gateways of India are the airports of Mumbai, Delhi, Bengaluru, Hyderabad and Chennai. Airports in cities are new or continue to develop. Delhi announced the brand new international terminal 3 during the 2010 Commonwealth Games & Bangalore launched the new airport in 2008. The Hyderabad airport was rated as one of the top 5 airports in the category 10. -15 million visitors per year. There are many direct flights connecting to cities in Europe, North America, the Middle East and Australia. Africa is also connected with Delhi and Mumbai.
For the second point of entry to India, consider Goa, Kolkata or the Malabar coast. There are many connections to the Malabar coast to cities like Kochi, Kozhikode and Thiruvananthapuram from the Middle East. Most major carriers in the Middle East offer one-stop connections to the coast from their Gulf hubs. Goa is a European tourist destination and is therefore connected by many European charter operators such as Condor, Edelweiss, Thomas Cook airlines and Thomson Airways. Kolkata is currently served by Emirates, Qatar Airways, Singapore Airlines and Thai Airways.
India has internationally renowned airlines like Air India (details; merged airlines formed by combining Air India). These airlines provide domestic flights. In recent years, the government has allowed private Indian airlines such as Indigo (details) to go international. There are daily flights to major hubs around the world from Delhi and Mumbai.
Air India usually offers the lowest rates for long-haul flights to India. In recent years it has gradually improved and has even been invited to join the Star Alliance, but there is still some way to go until it can be considered world class. Air India suffers from inconsistent customer service and its online booking/phone booking facility is up to standard.From the United States, United Airlines (details) provides daily non-stop service from Newark Airport To Delhi and Mumbai, India Air offers daily non-stop service to Delhi from JFK and ORD and Mumbai from EWR. American Airlines (details) offers daily non-stop service from Chicago to Delhi. Various European airlines provide service connections through their European hubs with most major US cities, and various Asian airlines provide connections from other major US cities. West Coast cities to India through their Asian hub.
From Europe and North America is able to use many European airlines such as Lufthansa (details), Finnair (details), British Airways (details), KLM Royal Dutch Airlines (details, Air France (details) and Virgin Atlantic (details). For long-term travelers (3-12 months), Swiss airlines (details) There are usually good deals from Switzerland with flight connections from major European and some US cities as well.
To save on tickets, consider connecting via Gulf countries, by Air Arabia (details) (Sharjah based low cost airline with several connections in Europe), Etihad (details) (especially if you need a one-way ticket or will be returning to Europe from an Asian country) via Abu Dhabi, as well as Emirates (details) via Dubai or Qatar Airways (details) via Doha. Obviously, airlines are also the easiest way to get from the Gulf countries themselves, along with Air India and Air India Express.
From East Asia and Australia, Singapore (served by Air India, which is a low-cost subsidiary of Air India Express details), as well as Singapore Airlines (details), which is a subsidiary of Silk Air details) and low-cost subsidiary Tiger Airways details) is arguably the best connection to India with flights to all major cities and many smaller ones. Due to its low-cost distance from Southeast Asia and vice versa, low-cost Malaysian airline AirAsia details) is usually the best choice (if booked in advance, one-way fares are normally under $100, sometimes less than $50, they have connections from China, Australia and most of Southeast Asia). They fly from Kuala Lumpur into New Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Kochi and Tiruchirapalli. If you are going from/to Thailand, Air India Express flies from Chennai and Kolkata to Bangkok. Air India and Thai Airways details) fly from there to wider range of Indian cities also. Most recently, Silk Air details) start direct flights from Singapore to Hyderabad good. Recently, IndiGo, an Indian low-cost airline, has started service with Singapore, Bangkok, Dubai, and Singapore. Muscat.
By train
By car
By bus
By boat
Go
Visit
If you really want to see all the valuable attractions in India, a tourist visa of six months will suffice. There are more tourist attractions in India than can be mentioned in a book. Most of the countries in India already have more than ten tourist destinations and there are cities that cannot be fully experienced even in a full week. Not forgetting that some states of India are bigger than most of the countries in the world and there are twenty-eight states in India.
- Taj Mahal:. The Taj Mahal is recognized as "jewel of Islamic art in India and is one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world heritage" It's actually bigger and more monumental than what it looks like in the photo.
- Agra: A majestic city, with historical sites like Agra . fortress majestic and beautiful red Taj Mahal.
- Delhi: The capital and center of India, which is both modern and historical. Having monuments like the Red Fort and Qutub Minar, it also offers modern amenities to visitors. Delhi also hosted the 2010 Commonwealth Games, and is less polluted than most ares of India.
- Varanasi: Hindu ritual religion, some re-harking to the Vedic age, 5,000 years ago, Varanasi is the world's oldest city and the birthplace of Hinduism. Don't miss the Ganga Aarti evening.
- Tiger, remember you'll need a lot of luck to see a tiger, but your chances of seeing a tiger are pretty good in Bandhavgarh nice Ranthambore tiger reserve.
- Lion, Gir Forest and Wildlife National Park Sanctuary (also known as Sasan-Gir, ગીર ) is the only home of the pure Asian Lion.
- Sundarbans. Largest mangrove forest and delta in the world. Home to the famous Royal Bengal tiger and crocodile estuary.
- Mountain resorts. India is home to a number of remarkable, scenic and stunning hill stations such as Shimla, Mussorie, Darjeeling, Nainital, Almora, Shillong, Mt.Abu and Ooty.
- Sangla . Valley. Considered one of the most beautiful valleys of the world located in the upper regions of the state of Himachal Pradesh. It is incredibly scenic with photogenic landscapes and unforgettable landscapes.
- Le H. Be on top of the world. One of the most densely populated cities in the world. It gives a different idea of complete elevation with unbelievable landscape.
- Srinagar. It is the capital of the state of Jammu and Kashmir during winter. Very beautiful city in the middle of the Himalayas with a very beautiful Dal lake in it.
- Jammu. It is the capital of the state of Jammu and Kashmir during the summer. Jammu city is also known as "Temple City" because it has many temples and shrines like Vashno Devi.
- Gangtok. The capital city of the state of Sikkim. Gangtok is a ravishing hill station located among the many-hued mountains of Sikkim.
- Goa. Ruled by Portugal for over 400 years, Goa is a kind of city that blends Indian and Portuguese cultures. Quite a different kind of place altogether, Goa is full of beautiful beaches and tourists flock.
- Pondicherry. Pondicherry has been a French colony for more than two hundred years and has very much seen French influence throughout its territory. Bây giờ khách du lịch thường đổ có cho đạo tràng tâm linh hay quán rượu thú vị và các bên.
- Bishnupur. Nằm ở Tây Bengal, nó là nơi có những ngôi đền đất nung nổi tiếng và một trung tâm tuyệt vời cho cổ điển Bishnupur Gharana âm nhạc. Không quên để mua một con ngựa Bankura làm terracota (đó là biểu tượng cho thủ công mỹ nghệ Ấn Độ).
- Tirupati Balaji. Nếu bạn muốn nhìn thấy sự phong phú vật chất của một cơ sở tôn giáo, hãy thăm ngôi chùa này. Nó được coi là ngôi chùa giàu nhất thế giới và một ngôi chùa không theo phong cách Ấn Độ. Nó nằm ở bang Andhra Pradesh.
- Nalanda. Liên quan đến Phật giáo, đó là trường đại học lâu đời nhất của thế giới sau này bị phá hủy hoàn toàn trong cuộc xâm lăng của người Hồi giáo Ấn Độ. Điểm tham quan quan tâm Phật giáo như Pavapuri và Rajgir là trong vùng lân cận.
- Chùa Vàng. Một ngôi chùa thực tế được dát vàng là một trong những ngôi đền linh thiêng nhất của đạo Sikh của. Trông rất thanh thản đầu vào buổi sáng.
- Khajuraho. Được cho là nơi sinh của Kamasutra, Khajuraho có đầy đủ các ngôi đền với tác phẩm điêu khắc khiêu dâm tất cả xung quanh họ. Một trong những thú vị nhất và ít nói về các khía cạnh của văn hóa Ấn Độ giáo.
- Kochi. Các bãi biển hẻo lánh và đẹp mê hồn, Kochi là một trong những nhất sau khi tìm địa điểm du lịch. Đó là khuyến khích đến thăm các thành phố xung quanh bãi biển của Kochi. Không quên để trải nghiệm backwaters của Kerala trong một nhà thuyền.
- Andamans. Đảo lãnh thổ xinh đẹp của Ấn Độ trong vịnh Bengal, hải đảo Andaman có thể được coi là một trong những điểm đến hòn đảo tốt nhất trên thế giới.
- Jaisalmer. Một thành phố nằm ở giữa sa mạc, Jaisalmer là một nơi để đi để xem xem đẹp của mặt trời sa mạc nguyên sáng của sa mạc Thar.
==Ngôn ngữ== giàu
Shopping
Expense
Food
Ẩm thực Ấn Độ rất đa dạng, về thành phần, hương vị và cách chế biến khác biệt theo từng vùng. Gạo và bột mì là hai thực phẩm chính của nước này. Ấn Độ nổi tiếng về số lượng các món chay và không chay như cuisine. Thực phẩm nhiều gia vị và đồ ngọt rất phổ biến ở Ấn Độ.
Drinks
Accommodation
Learn
Do
Safe
Medical
To respect
Contact
Reference
Template:Reference
